After surgery, it is recommended that the patient practice basic stretching exercises (neuro-flossing) to ensure proper recovery.
How to Explain Cervical Neuroplasty?
The Reason for the Pain
The movement of healthy nerves within the spinal canal should not hurt, but the pain is often felt when they are restricted or swollen. Nerves can become irritated and swollen when they are compressed, such as by a bulging disc, an osteophyte, or scar formation following surgery or leaking disc. Restrictions can also be caused by the presence of scar tissue. As individual nerve roots exit the vertebrae, they pass through an opening called the neural foramen. During the exercise of the head and neck, the nerves will move slightly in and out of the foramen. When nerve movement is compromised, this normal sliding movement is no longer possible. The lysis procedure is designed to release the tension on the nerve, restore mobility and thereby reduce the radiating pain.
Cervical Neuroplasty, the procedure
During the cervical epidural lysis of adhesions procedure also known as cervical neuroplasty, a needle will be generally placed laterally around the area of T1 or T2 and a contrast dye will be injected to outline scarring around the pain-generating nerve root.
A physician will then introduce an Epimed steerable spring-guided catheter under X-ray guidance to the source of the pain. Medications are then injected to open up the affected region by fluid dissection. A steroid and hyper-osmolar solution in some cases may be injected to help calm the swollen “angry” nerve root. The medical procedure performed is just one step in the process toward pain relief. Physical therapy is the next critical component to further ensure improved, lasting recovery.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is highlight recommended to keep the joint flexing and retard the formation of new adhesions. The stretching exercise outlined there is designed to complement the clinical procedure. They help to regain and maintain the movement of the nerves in and out of the spinal canal. This type of exercise-induced nerve root movement is referred to as Neural Flossing™.
Before initiating the exercise, our patient should dress in comfortable, non-restrictive clothing. This will allow the stretching to be correctly performed and provide the patient with the full benefits of the Neural Flossing™ technique.
Cervical Neural Flossing, improve the recovery with those specific stretching exercises
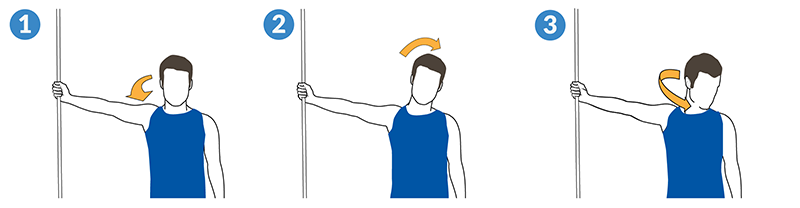
In order to complete this exercise correctly, each stage must be performed in sequence.
- Standing erect, firmly grasp a stable surface (ex. door frame) with outstretched arm. Slowly push elbow and shoulder forward.
- Next, slowly tilt head in opposite direction from outstretched arm to achieve gentle tension. It is important that you tilt your head away from the affected area.
- Finally, rotate chin towards opposite shoulder as is comfortable. Hold this final position for approximately 20-30 seconds. It is important that you maintain gentle pressure in order to benefit from the cervical Neural Flossing™ effect.
Although results may not occur immediately, continued practice of this stretching exercise produces the best long-term outcome. Increased flexibility and strength may emerge after one month.
It is important to perform this exercise with increasing duration from 20-30 seconds. The prolonged or sustained stretch of the affected nerve results in pulling the nerve through the foramen maintaining a clear pathway.
This exercise should be carried out 2-3 or more times a day with each session lasting no longer than 3 to 5 minutes.
For chronic pain sufferers, this stretching exercise should be continued indefinitely to prevent the restriction of affected nerve roots and the resulting return of pain
Print the Post Cervical Neuroplasty Rehabilitation Guide for patients
Download and print the one-page patient guide about Cervical Neural Flossing, with pictures and step-by-step stretches to do. A useful guide to offer to your patients to help them in their recovery.
Click here to download the Guide.
Patient education, other tools
To Increase the patients’ understanding of the procedures, Epimed has developed a range of tools to facilitate comprehension and reinforce exchanges and trust with patients. What is understood is better accepted. With this in mind, Epimed offers anatomical charts and models perfectly adapted to the field of patient education.
 Sign in
Sign in
 Create Account
Create Account